Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: To visualize the colon and surrounding organs.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: This is the most common title for CT scans.
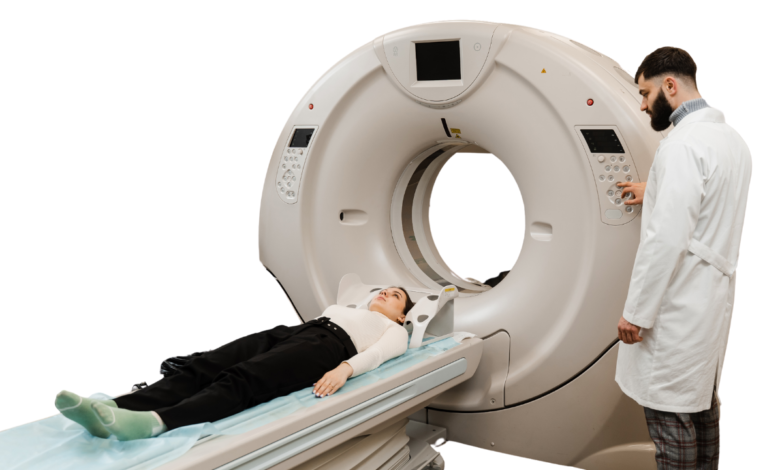
What is Computed Tomography (CT) Scan?
A CT scan, also known as a CAT scan, is an imaging test that uses X-rays to create detailed images of the body. It can be used to visualize the colon and surrounding organs.
Why Computed Tomography (CT) Scan is required?
CT scans are often used to:
- Diagnose colon cancer or other conditions: They can help identify tumors, polyps, or other abnormalities in the colon.
- Stage colon cancer: CT scans can help determine the extent of the cancer, including whether it has spread to other organs.
- Monitor treatment: CT scans can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for colon cancer or other conditions.
- Evaluate symptoms: They can help investigate symptoms like abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, or rectal bleeding.
which are the method of Computed Tomography (CT) Scan ?
· Standard CT scan: This involves lying on a table while the machine rotates around you, taking images from multiple angles.
· Multidetector CT (MDCT) scan: This uses multiple detectors to acquire images more quickly and with greater detail.
who should go for Computed Tomography (CT) Scan ?
Your doctor may recommend a CT scan if you have:
- Symptoms of colon cancer, such as changes in bowel habits, blood in your stool, or abdominal pain.
- A family history of colon cancer or other risk factors.
- A previous diagnosis of colon cancer or polyps.
What are the results of Computed Tomography (CT) Scan ?
A CT scan can reveal:
- Tumors: CT scans can help detect both benign and malignant tumors in the colon.
- Polyps: These are small growths in the colon that can be precancerous.
- Metastases: CT scans can help determine if cancer has spread to other organs.
- Other abnormalities: CT scans can also identify other conditions such as diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or infections.
What are the components of Computed Tomography (CT) Scan ?
A CT scan typically involves:
- Preparation: You may be asked to fast or avoid certain foods before the test.
- Positioning: You will lie on a table while the machine rotates around you.
- Injection of contrast material: In some cases, a contrast material may be injected into your bloodstream to improve the visibility of certain structures.
- Imaging: The machine will take images from multiple angles.
- Interpretation: A radiologist will interpret the images and provide a report to your doctor.